Basic information
LLPS related evidences
| Publication note | Here we assembled mitochondrial nucleoids in vitro and show that mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) undergoes phase separation with mtDNA to drive nucleoid self-assembly. Moreover, nucleoid droplet formation promotes recruitment of the transcription machinery via a special, co-phase separation that concentrates transcription initiation, elongation and termination factors, and retains substrates to facilitate mtDNA transcription. (Organism: Homo sapiens; Cell line: MEF cells) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material state | liquid : The recovery of the TFAM signal demonstrates that TFAM droplets are dynamic and possess liquid-like fluidity. These droplets could undergo fusion in vitro, which is a characteristic of liquid droplets. | ||
| LLPS region | _ | Key domains | linker domain, high mobility group A(HMG-A) domain, high mobility group B(HMG-B) domain, C-tail : The C-tail was dispensable for droplet formation, whereas mutants lacking the linker domain did not show any droplets. Three domains, HMG-A, HMG-B and linker domain of TFAM, are responsible for DNA binding. The phase separation of the TFAM-DNA complex may be driven by multivalent effects through multiple binding sites of TFAM on DNA. Mutants containing only one of the three domains did not show clear separation with DNA. |
LLPS partner
| Protein partner | POLRMT,TFB2M,TEFM,MTERF1 ( O00411,Q9H5Q4,Q96QE5,Q99551 ) |
The recombinant POLRMT and TFB2M proteins did not display any phase separation individually or with added DNA, but both underwent phase separation in the presence of TFAM with ND1 or D-loop DNA that contains regulatory elements and a light-strand promoter. TFB2M and POLRMT formed a co-phase separation with TFAM-DNA droplets. TFAM and DNA formed the core of the droplet, and POLRMT and TFB2M encircled the droplet of the nucleoid, indicating a co-phase separation similar to the phase separation of the nucleolus. |
|---|---|---|
| RNA partner | _ |
_ |
| Others | ND1 DNA,mtDNA,UTP |
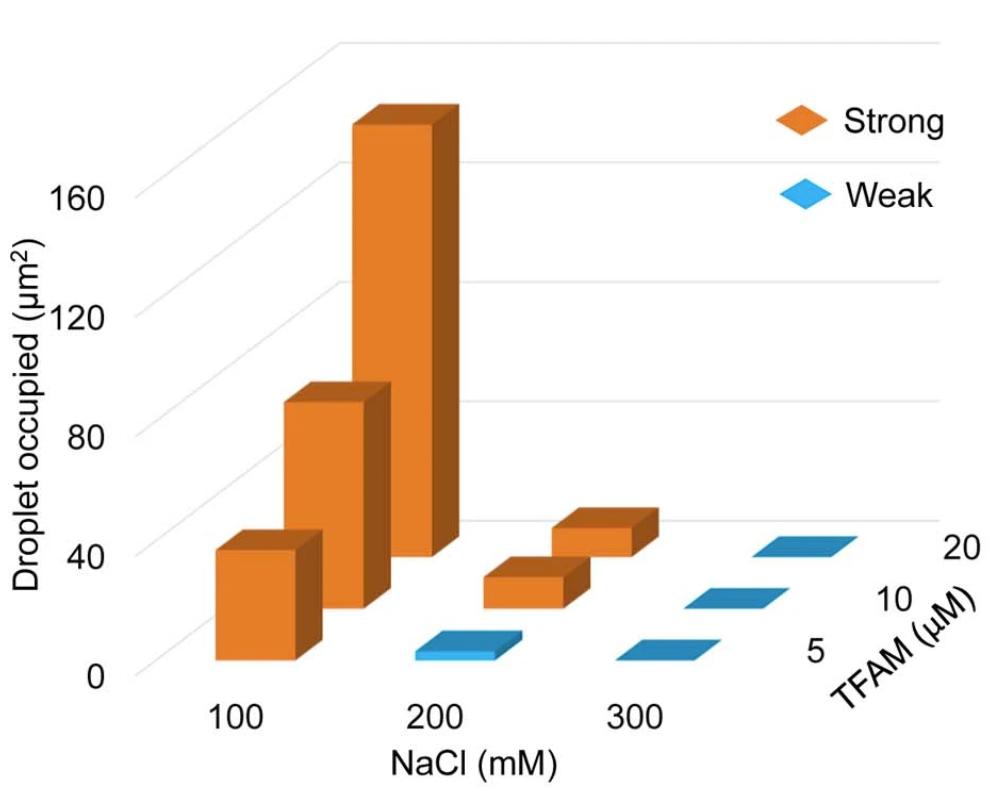
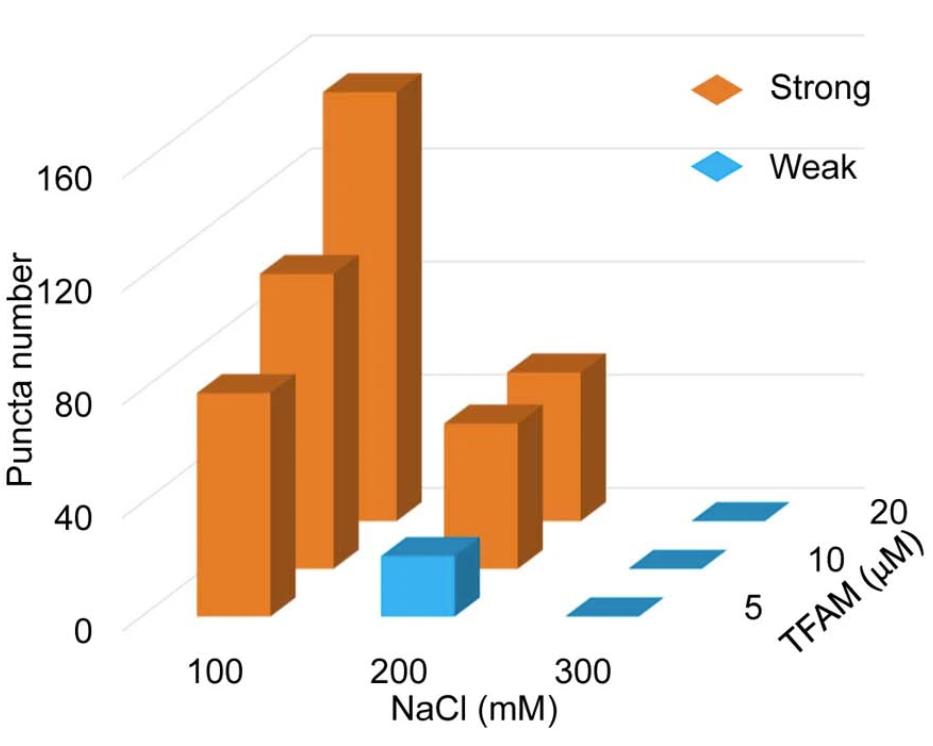
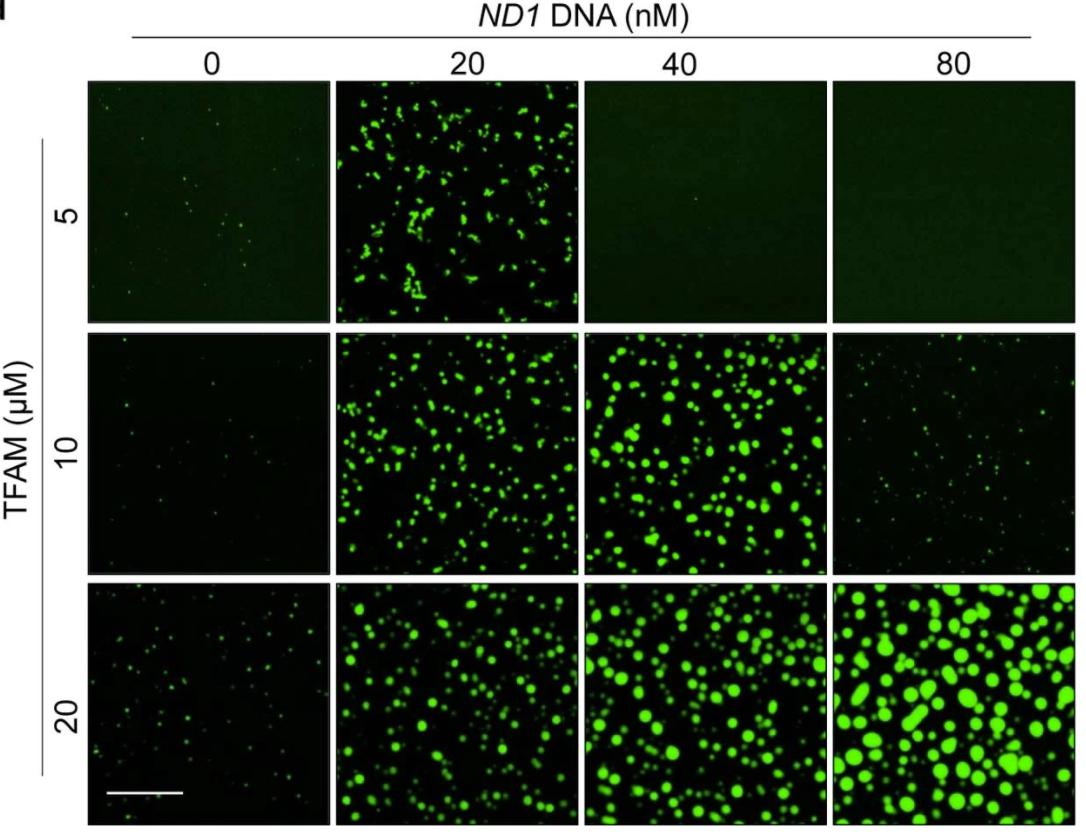
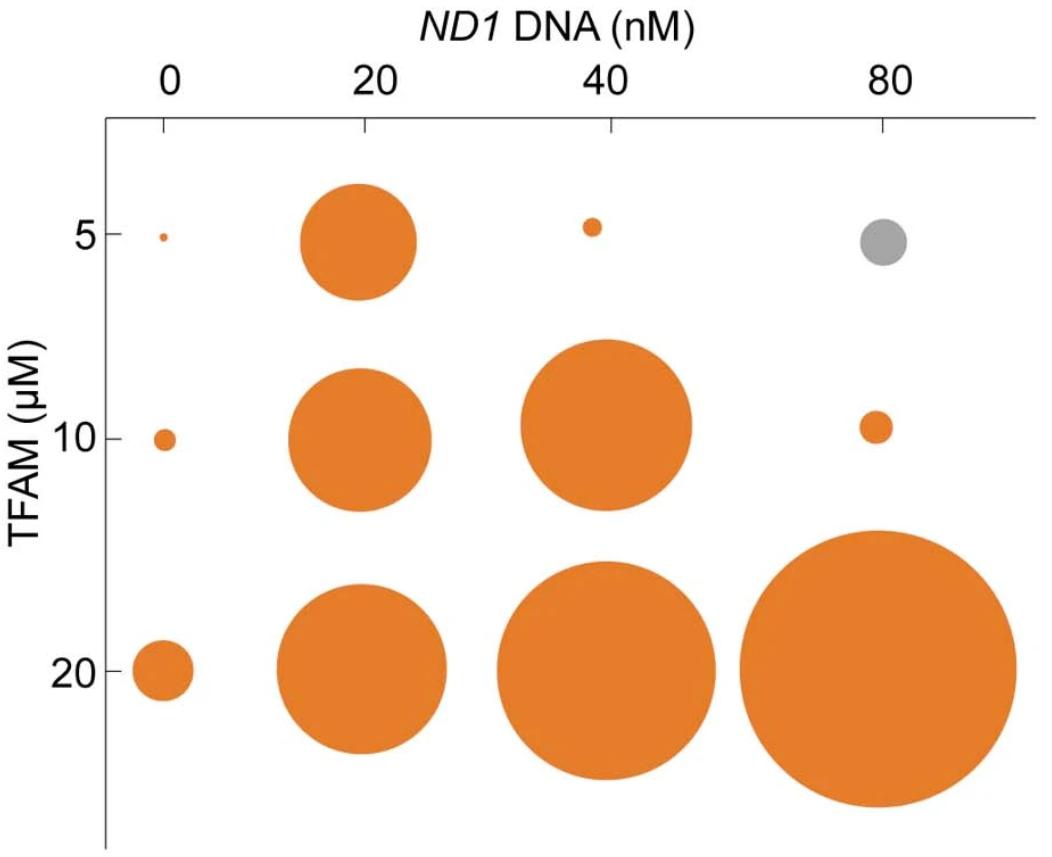
We observed robust formation of droplets when mixing ND1 DNA with TFAM at 100 mM NaCl, and TFAM colocalized well with DNA as the Pearson’s colocalization oefficient is higher than 0.82. Meanwhile, both the diameter and occupied area of droplets increased with increasing DNA concentration, indicating the self-assembly of nucleoid-like droplets is DNA concentration-dependent. However, droplet formation was suppressed at higher concentrations of DNA, indicating a saturation ratio for TFAM-DNA co-phase separation, which is commonly observed in phase separation driven by multiple components. Robust formation of droplets occurred following the addition of mtDNA to TFAM. Surprisingly, the occupied area and number of droplets increased with increasing amounts of mtDNA, while the droplet size remained largely constant. UTP may also be enriched by TFAM-DNA in a phase separation-dependent manner. |
LLPS regulation
| PTM | _ |
_ |
|---|---|---|
| Mutation | _ |
_ |
| Alternative splicing | _ | |
| Repeat | _ | |
| Oligomerization | _ | |