Basic information
| PhaSepDB ID | psself353 | Reference | 33771451,33333019 | Uniprot Entry | Q15648 | Gene names | MED1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | PS-self | Location | Nucleus | MLO | _ | ||
LLPS related evidences
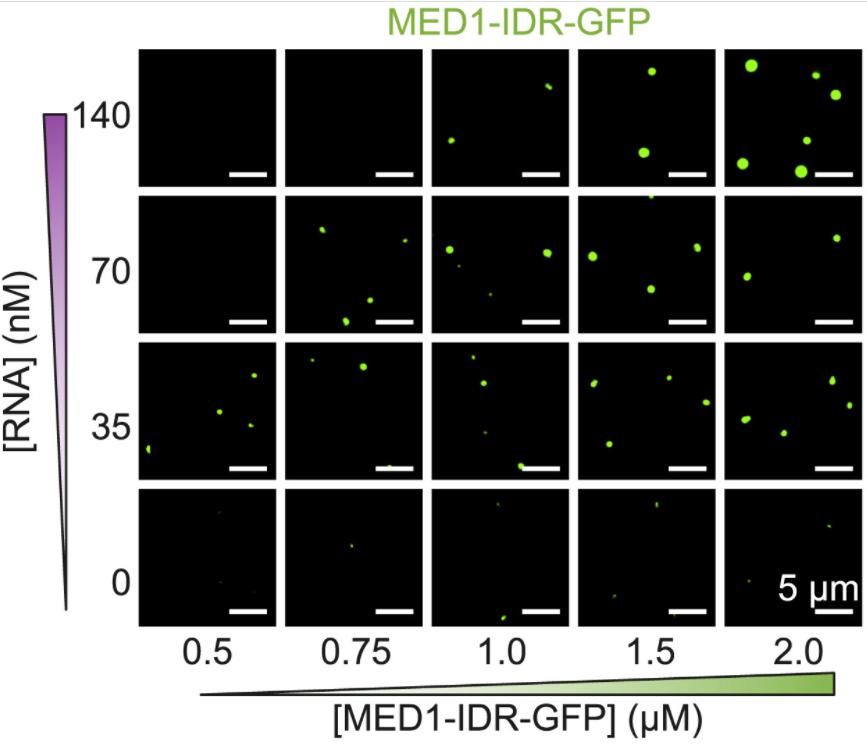
| Publication note | Addition of 6–400 nM of each of these RNAs to 1,000 nM MED1-IDR (protein:RNA ratios = 167:2.5) stimulated formation of MED1-IDR condensates at low RNA concentrations and dissolved MED1-IDR condensates at higher RNA concentrations. BRD4 is another key component of transcriptional condensates, and BRD4-IDR protein exhibits condensate behaviors very similar to those of MED1-IDR; the effects of increasing RNA levels on formation and dissolution of BRD4-IDR condensates were very similar to those observed for MED1-IDR. (Organism: Homo sapiens; Cell line: V6.5 murine embryonic stem cells) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material state | liquid : Condensates exhibited internal dynamic reorganization with apparent diffusion coefficients 3–5 ± 0.8 × 10−2 μm2/s, consistent with liquid-like behavior. | ||
| LLPS region | IDR region | Key domains | intrinsically disordered region(IDR) : Addition of 6–400 nM of each of these RNAs to 1,000 nM MED1-IDR (protein:RNA ratios = 167:2.5) stimulated formation of MED1-IDR condensates at low RNA concentrations and dissolved MED1-IDR condensates at higher RNA concentrations. the effects of increasing RNA levels on formation and dissolution of BRD4-IDR condensates were very similar to those observed for MED1-IDR |
LLPS partner
| Protein partner | _ ( _ ) |
_ |
|---|---|---|
| RNA partner | Pou5f1 enhancer RNA,Trim28 enhancer RNA,Nanog enhancer RNA |
diverse RNAs are capable of stimulating MED1-IDR condensate formation when present at relatively low levels and dissolving MED1-IDR condensates at high levels. |
| Others | _ |
_ |
LLPS regulation
| PTM | _ |
_ |
|---|---|---|
| Mutation | _ |
_ |
| Alternative splicing | _ | |
| Repeat | _ | |
| Oligomerization | _ | |