Basic information
LLPS related evidences
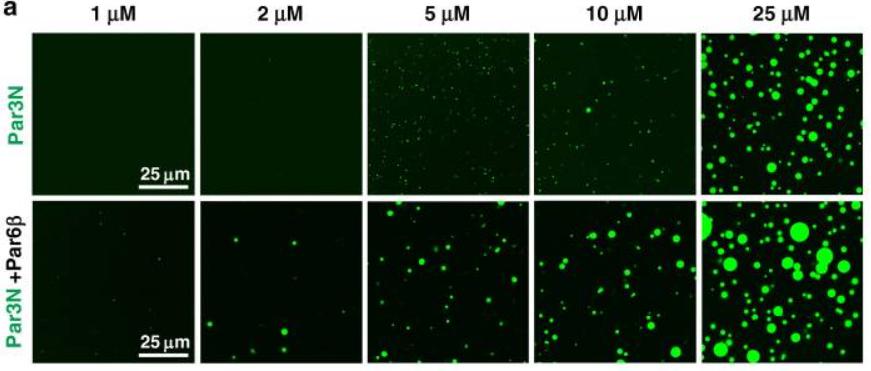
| Publication note | Here we show that the Par complex exhibits cell cycle-dependent condensation in Drosophila neuroblasts, driven by liquid-liquid phase separation. The open conformation of Par3 undergoes autonomous phase separation likely due to its NTD-mediated oligomerization. Par6, via C-terminal tail binding to Par3 PDZ3, can be enriched to Par3 condensates and in return dramatically promote Par3 phase separation. aPKC can also be concentrated to the Par3N/Par6 condensates as a client. Interestingly, activated aPKC can disperse the Par3/Par6 condensates via phosphorylation of Par3. Perturbations of Par3/Par6 phase separation impair the establishment of apical-basal polarity during neuroblast asymmetric divisions and lead to defective lineage development. (Organism: Mus musculus; Cell line: COS-7 cells) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material state | liquid,hydrogel : Those Par3N/Par6β droplets transitioned into gel-like structures over time, and the droplets rarely fused together after 20 min. | ||
| LLPS region | 1-371 | Key domains | PDZ-binding motif (PBM) : Par3N specifically binds to Par6β via the PDZ3–PBM recognition. |
LLPS partner
| Protein partner | Par3,aPKC ( Q9Z340,Q62074 ) |
Par6, via C-terminal tail binding to Par3 PDZ3, can be enriched to Par3 condensates and in return dramatically promote Par3 phase separation. |
|---|---|---|
| RNA partner | _ |
_ |
| Others | _ |
_ |
LLPS regulation
| PTM | _ |
_ |
|---|---|---|
| Mutation | _ |
_ |
| Alternative splicing | _ | |
| Repeat | _ | |
| Oligomerization | _ | |