Basic information
LLPS related evidences
| Publication note | Here, we demonstrated that autophagic degradation of PGL granules is specified by phase separation and transition that are controlled by SEPA-1, EPG-2, and PTMs. SEPA-1 promotes LLPS of PGL-1 and PGL-3. EPG-2 determines the size of droplets and also converts them into gel-like structures. (Organism: Caenorhabditis elegans; Cell line: C.elegans embryos) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material state | liquid,hydrogel : EPG-2/SEPA-1/PGL-1/-3 liquid-like droplets develop gel-like characteristics over time, including impaired fusion capability, increased resistance to high salt, and reduced dynamics. | ||
| LLPS region | 1-350,1-702 | Key domains | PGL-3-binding domain : The region in SEPA-1 that promotes LLPS of PGL-1/-3 was delineated to the N-terminal region, which contains the PGL-3-binding domain. |
LLPS partner
| Protein partner | PGL-1,PGL-3 ( Q9TZQ3,G5EBV6 ) |
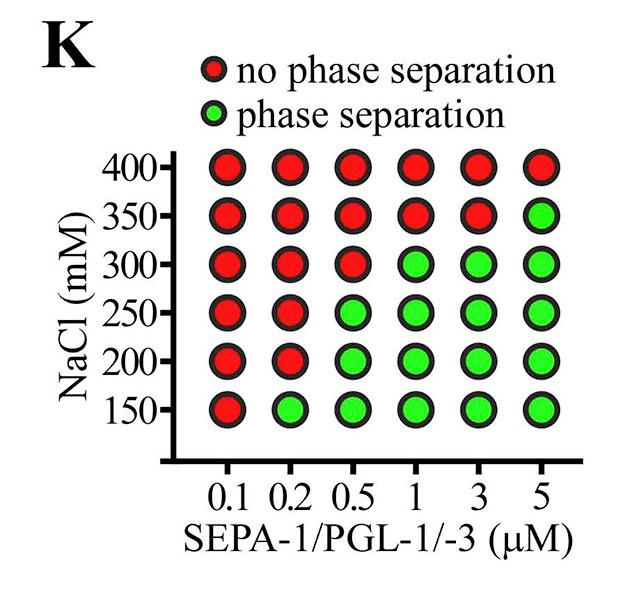
Purified SEPA-1 failed to phase separate. Co-addition of SEPA-1 promoted LLPS of PGL-3 and PGL-1/-3, but not PGL-1 alone. In the presence of SEPA-1, larger droplets formed and more PGL-1/-3 proteins partitioned into droplets. |
|---|---|---|
| RNA partner | _ |
_ |
| Others | _ |
_ |
LLPS regulation
| PTM | _ |
_ |
|---|---|---|
| Mutation | _ |
_ |
| Alternative splicing | _ | |
| Repeat | _ | |
| Oligomerization | _ | |